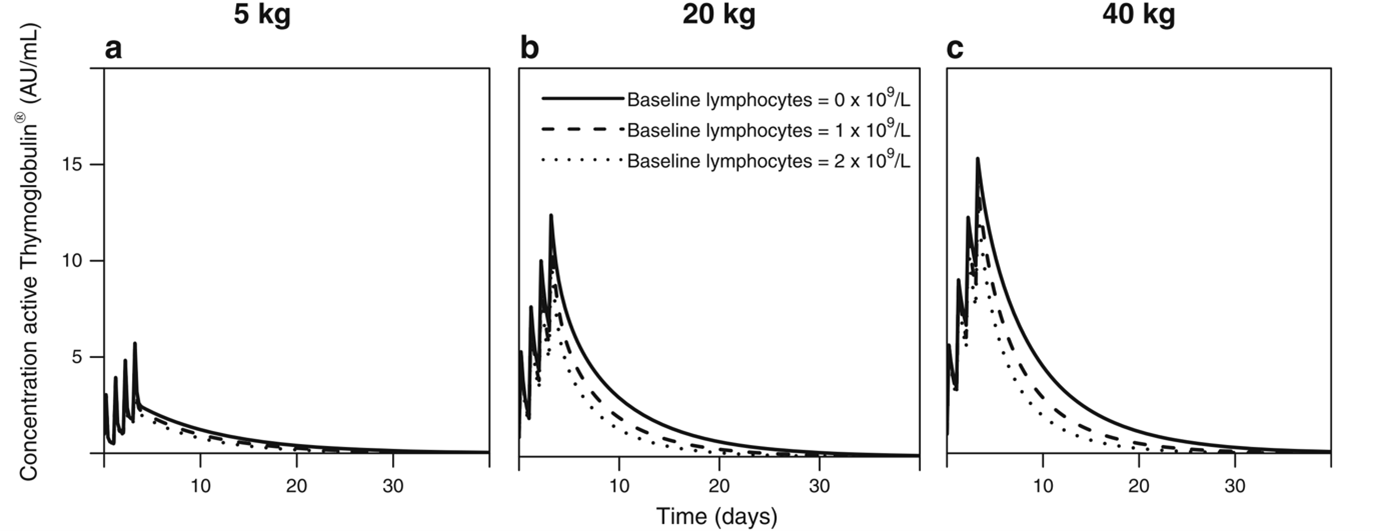
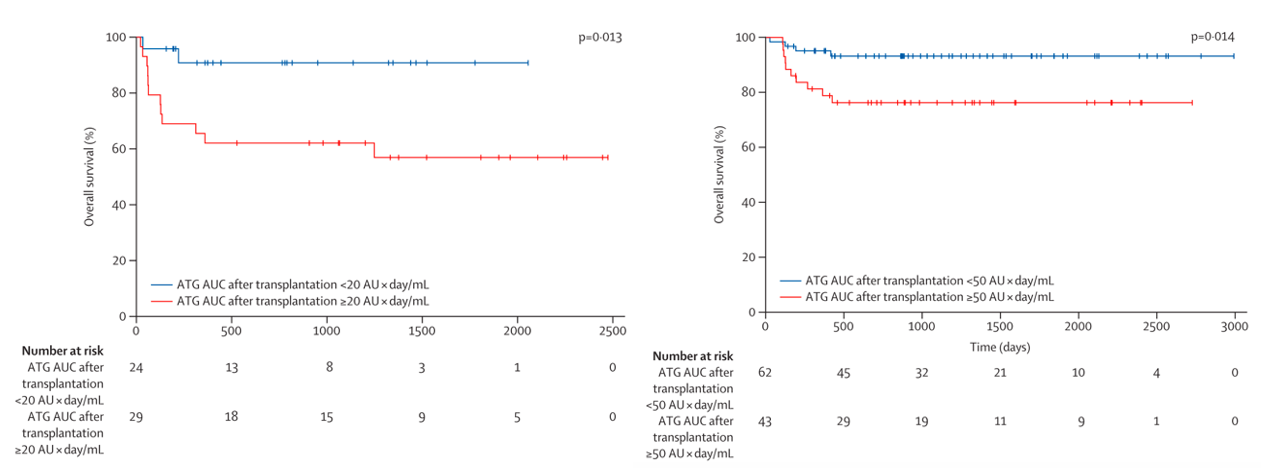
Results from 2, 3 and 4 were combined to develop a model-based (MB) dosing (MBD) algorithm for ATG aiming for optimal exposures that would lead to potent T-cell recovery and reduced mortality. The PARACHUTE-trial (Admiraal, Lancet Haem 22) evaluated the MB-dosing in a single-arm open label phase II trial, powered for T-cell recovery. The trial showed a marked improvement in successful T-cell recovery from 50% (historical controls) to 75% of pts. No increase in GvHD was observed.
We combined the recent analysis of the 5-year follow-up results of the PARACHUTE combining with real-world data using the same regimen (patients from Utrecht and New York; manuscript in preparation, presented at ASTCT Tandem 2024). Here, MB-dosing improves OS as compared to historical controls (Figure 3). The incidence of cGvHD and GF is markedly lower with MB-dosing. Importantly, successful CD4IR was strongly associated with improved TRM.
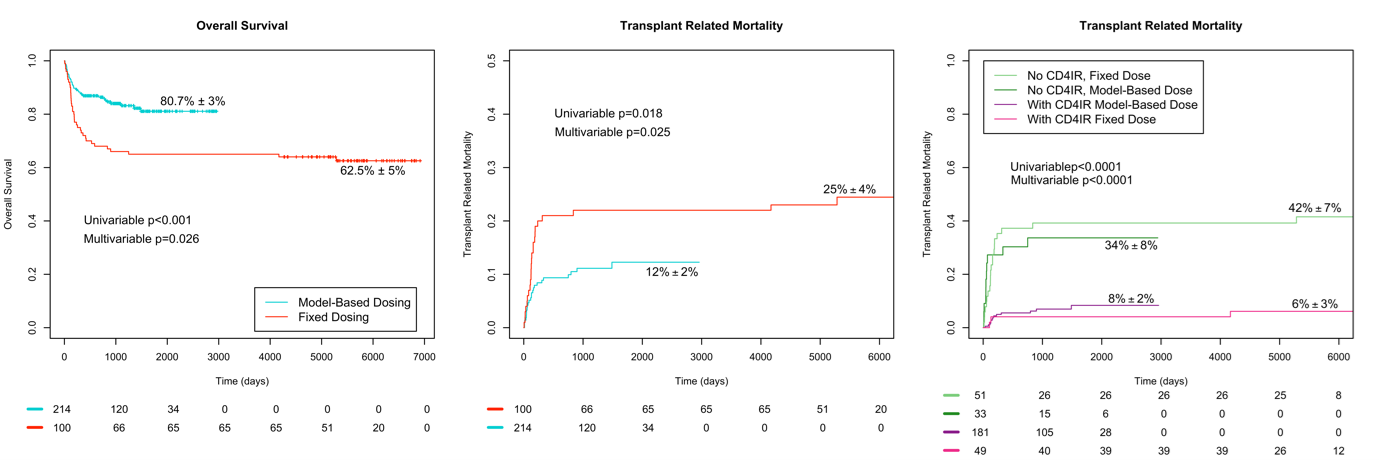
Figure 3: Updated results of PARACHUTE with real-world data (Model-based dosing) versus historical controls (Fixed dosing). Panel A: overall survival according to treatment group; panel B: transplant related mortality according to treatment group; panel C: transplant related mortality according to CD4 T-cell recovery (CD4IR) and treatment group. Confidential data, submitted